[ad_1]
Hibernating bears can’t assist us escape lengthy aircraft flights or unforgiving winters — however they could assist us forestall blood clots.
The bears, throughout hibernation, forestall blood clots in their very own our bodies by preserving a low stage of a key protein of their blood, in response to a brand new research revealed in Science.
Now, the researchers hope their findings may be utilized to growing future medications in people that may mimic the best way nature prevents blood clots in bears.
BLOOD CLOT SYMPTOMS TO LOOK OUT FOR
The researchers in contrast blood samples from 13 wild brown bears through the winter whereas they have been hibernating with blood samples through the summer season when the bears have been extra energetic.
They particularly checked out platelets — which assist the blood kind clots — discovering that the hibernating bears’ blood samples had platelets that have been much less prone to clump collectively than the samples taken of the bears through the summer season.

A grizzly bear is proven foraging in Glacier Nationwide Park in Montana. Whereas hibernating bears can’t assist us escape lengthy aircraft flights or unforgiving winters — they could assist us forestall blood clots, in response to a brand new research that regarded on the blood samples of each hibernating bears and energetic bears. (iStock)
The analysis group additionally discovered that when the platelets did clot, they did so extra slowly.
The research discovered {that a} key distinction within the bears’ winter and summer season blood samples have been ranges of a protein known as warmth shock protein 47 — or HSP47 — in platelets.
WHO IS AT RISK FOR DEVELOPING BLOOD CLOTS?
This protein is often present in cells that kind connective tissues like bone and cartilage, in addition to platelets, the place HSP47 attaches to a protein known as collagen that helps them stick collectively to kind a clot.
The research discovered a key distinction within the bears’ winter and summer season blood samples.
The hibernating bears had roughly one-fiftieth of the quantity of HSP47 present in energetic animals.
The analysis was accomplished by cardiologists on the Ludwig Maximilian College of Munich, who teamed up with a Scandinavian group and different researchers to check hibernating brown bears in Sweden, in response to Science.
Blood consists of purple blood cells, white blood cells and platelets that float within the liquid portion of the blood referred to as plasma. After we bleed, this initiates the coagulation — or clotting cascade — that prompts proteins on platelets to clump to fill the opening within the blood vessel, in order that we cease bleeding. (iStock)
The researchers additionally carried out lab experiments with mice to substantiate that HSP47 was the rationale behind the hibernating bears’ lack of blood clots.
The mice that lacked the HSP47 protein had fewer clots and decrease ranges of irritation in comparison with animals who had HSP47.
BE WELL: WHY IT’S WISE TO DITCH THE ELEVATOR AND TAKE THE STAIRS
As well as, researchers found that pigs that had lately given beginning — animals which might be fairly motionless for as much as 28 days whereas feeding their piglets — additionally had decrease HSP47 ranges in contrast with energetic pigs.
The findings additionally utilized to individuals who have long-term immobility points.

Pigs that had lately given beginning — animals that stay fairly motionless for as much as 28 days whereas feeding their piglets — additionally had decrease HSP47 ranges, in contrast with energetic pigs, researchers discovered. (iStock)
Individuals with spinal cord injuries additionally had low ranges of HSP47. As well as, 12 wholesome volunteers had decrease HSP47 ranges after 27 days of relative immobility in a bed-rest research.
How the physique kinds clots
“After we lower ourselves, we bleed as a result of blood vessels beneath the pores and skin tear,” Dr. Mikkael Sekeres, chief of the division of hematology at Sylvester Most cancers Heart within the College of Miami in Miami, Florida, advised Fox Information Digital. (He was not concerned within the analysis.)
“They then launch chemical substances that, in flip, activate proteins within the plasma,” added Sekeres, writer of the ebook “Medication and the FDA: Security, Efficacy, and the Public’s Belief.”
This course of can generally get activated inappropriately even when there isn’t any bleeding — inflicting “deep vein thrombosis.”
Blood consists of purple blood cells, white blood cells and platelets that float within the liquid portion of the blood referred to as plasma, in response to Cleveland Clinic.
BLOOD DONATIONS THIS WINTER: AMERICAN RED CROSS URGES PEOPLE NOT TO FORGET TO DONATE
After we bleed, this initiates the coagulation — or clotting cascade — that prompts proteins on platelets to clump to fill the opening within the blood vessel, so we cease bleeding, Sekeres defined.
Deep vein thrombosis may be harmful
This course of can nonetheless generally get activated inappropriately even when there isn’t any bleeding, inflicting “deep vein thrombosis,” or DVT.
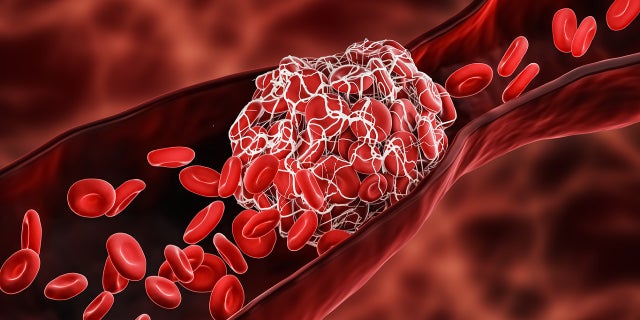
Blood consists of purple blood cells, white blood cells and platelets that float within the liquid portion of the blood referred to as plasma, in response to Cleveland Clinic. After we bleed, this initiates the coagulation — or clotting cascade — that prompts proteins on platelets to clump to fill the opening within the blood vessel in order that we cease bleeding, one physician defined. (iStock)
Frequent signs of DVT embody swelling, ache, tenderness and redness of the pores and skin within the decrease leg, thigh, pelvis and generally even the arm, in response to the Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention (CDC).
Some 50% of individuals with DVT won’t have any signs, the company added.
Individuals can usually kind within the massive veins within the legs, “which might turn out to be life-threatening in the event that they journey to very important organs just like the lungs — termed [a pulmonary] embolism,” added Sekeres.
A “extended lack of exercise” — comparable to throughout lengthy aircraft flights — could cause the blood to pool and make folks extra in danger for DVTs.
A pulmonary embolism, which is essentially the most critical complication of DVT, happens when part of the clot breaks off and travels by way of the bloodstream to the lungs, blocking very important blood circulate, per the CDC.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
Sekeres famous that “extended lack of exercise” — comparable to throughout long plane flights — could cause the blood to pool and make folks extra in danger for DVTs.
Different threat components embody sure drugs, comparable to hormone therapies, surgical procedure or “inherited defects within the clotting cascade that encourage it to ‘activate,’” he added.

A industrial airliner cabin full of passengers. Well being consultants advise that folks stand up and transfer round sometimes on lengthy flights. Different good recommendation consists of stretching the ft and calves to assist blood circulate. (iStock)
The CDC advises that folks see a health care provider instantly if they’ve any signs of a DVT.
‘Potential goal’ for DVT treatment
Specialists might assist develop potential drugs that will goal HSP47 from attaching to proteins or immune cells that provoke clots, in response to a report on the research’s key findings.
Extra analysis is required to higher perceive how the human physique particularly regulates HSP47.
“We forestall the event of DVTs with drugs that block segments of the coagulation cascade, or that intrude with proteins on platelets, stopping the clot from forming,” Sekeres added.
“The protein HSP47 might be a possible goal for considered one of these drugs.”
Most animals use the identical proteins to not solely make clots however to forestall blood loss.
But the sequence of occasions resulting in forming a clot could fluctuate amongst species, in response to Science Information, an unbiased journal that experiences on the newest science.
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
Extra analysis is required to higher perceive how the human physique particularly regulates HSP47 — and the way being motionlessness over time motivates the physique to make much less HSP47, Science Information added.
Source link
