[ad_1]
Scientists have discovered that artificial intelligence could possibly be an efficient software in predicting pancreatic most cancers earlier than a single symptom seems, based on a research printed within the journal Nature Drugs on Could 8.
A workforce of researchers led by Copenhagen College Hospital in Denmark and Harvard Medical School in Boston accomplished a sweeping research to find out whether or not AI might flag an individual’s threat of creating the illness.
The outcomes exceeded their expectations, with the mannequin efficiently predicting threat as much as three years earlier than analysis.
PANCREATIC CANCER RATES ARE RISING FASTER AMONG WOMEN THAN MEN: NEW STUDY
In 2023, about 64,050 individuals within the U.S. will likely be recognized with pancreatic cancer and about 50,550 will die from the aggressive illness, the American Most cancers Society (ACS) says.
The five-year survival charge throughout all levels is simply 12% within the U.S.
Whereas early screening and detection can enhance outcomes, a overwhelming majority of circumstances are recognized at superior levels.

Scientists have discovered that synthetic intelligence could possibly be an efficient software in predicting pancreatic most cancers earlier than a single symptom seems, per a research printed within the journal Nature Drugs on Could 8. (iStock)
Within the research, the researchers used AI and machine learning methods to investigate medical information from six million sufferers in Denmark and three million sufferers within the U.S.
“AI is superb at studying from giant databases, even when they’re considerably noisy, however you want a number of information to ensure that it to be efficient,” research co-author Dr. Chris Sander, PhD, professor of cell biology at Harvard Medical Faculty, advised Fox Information Digital in an interview.
Solely a really small portion of these sufferers ended up creating pancreatic most cancers.
The researchers’ aim was to make use of AI to seek out the variations between the 2 paths — those that had been in the end recognized and people who remained disease-free.
“AI-based screening is a chance to change the trajectory of pancreatic most cancers.”
The know-how scanned the info for as much as 2,000 illness codes throughout every affected person’s medical historical past that would predict the likelihood of developing cancer inside a sure time-frame.
The timing of the ailments — a lot of which weren’t even associated to the pancreas — was an vital think about predicting threat.

Most medical doctors depend on imaging exams, endoscopic ultrasounds, tissue biopsies and blood exams for pancreatic screenings, based on the Mayo Clinic. (iStock)
“The research aimed to see whether or not the affected person was on a path to pancreatic most cancers,” stated research creator Dr. Søren Brunak, a Danish organic and bodily scientist on the College of Copenhagen, in an interview with Fox Information Digital.
Each affected person has an entire illness trajectory, Brunak defined, evaluating it to an “total film of all diagnoses and procedures.”
He added, “We weren’t simply asking which ailments the affected person had earlier than, but in addition in what order they appeared, so we might determine any predictive alerts.”
“We regarded for threat elements from their previous that may have an effect on whether or not they would get this uncommon type of most cancers.”
Stated Brunak, “We regarded for threat elements from their previous that may have an effect on whether or not they would get this uncommon type of most cancers.”
In the end, the aim was to learn the way pancreatic most cancers really develops, the biology behind it, which genes can predict threat and what different elements could make somebody predisposed to the illness, Brunak stated.
Potential to ‘enhance affected person outcomes’
When the researchers utilized their AI mannequin to foretell the 1,000 sufferers who had been on the highest threat, they discovered that about 320 of them finally developed pancreatic most cancers.
COULD A URINE TEST DETECT PANCREATIC AND PROSTATE CANCER? STUDY SHOWS 99% SUCCESS RATE
Totally different variations of the AI fashions predicted threat inside totally different time frames — six months, one 12 months, two years and three years earlier than analysis.
The accuracy elevated for the shorter time frames, Sander defined.
“Just like the climate, the prediction was extra correct one 12 months or one month out,” he stated. “The prediction for shorter time scales was fairly good.”

Jerry Springer, journalist, actor and speak present host, handed away on April 27 of this 12 months after a battle with pancreatic most cancers. (Getty Photos)
Dr. Harvey Castro, a Dallas, Texas-based board-certified emergency medication doctor and nationwide speaker on synthetic intelligence in well being care, was not concerned within the research however was impressed by its findings.
“The research’s outcomes have the potential to tell the design of surveillance packages for sufferers at elevated threat, which might enhance affected person outcomes and high quality of life,” he advised Fox Information Digital.
“The research can considerably influence remedy choices and affected person outcomes by specializing in the early detection of pancreatic most cancers,” he added.
Present screening strategies might miss circumstances
Early detection and remedy are key to enhancing pancreatic most cancers survival charges, consultants agree — however the present screening strategies have some key limitations, in addition they say.
Most medical doctors depend on imaging exams, endoscopic ultrasounds, tissue biopsies and blood exams, based on the Mayo Clinic.
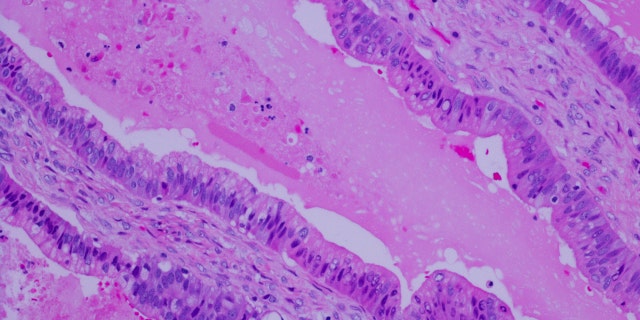
Metastatic pancreatic most cancers (proven) is most cancers that begins within the pancreas and spreads to different organs, mostly inside the stomach and to the liver, lungs, bones and mind. (iStock)
Some of these focused exams are normally not performed till a doctor already suspects {that a} affected person may need the illness.
Moreover, with the excessive price of such screenings as MRIs, CT scans and ultrasounds, these subtle exams is probably not obtainable to individuals who don’t have signs or confirmed threat elements, famous Sander, the research’s co-author.
“If we are able to transfer even a fraction of most cancers care to earlier detection and remedy, it’s going to have an enormous profit.”
One other drawback with the present screenings is that they’re infamous for producing false positives, Brunak identified.
“This overloads the well being care system and sufferers get involved with out cause,” he stated.
The brand new research means that by making use of AI-based screening to a broader inhabitants, those that had been unknowingly at a better threat of the lethal illness might get earlier diagnoses and quicker remedy earlier than the most cancers progresses to extra superior levels.
‘Contemplate rolling it out to broader neighborhood’
The present research was retrospective, wanting again at present information units over a time frame up to now.
Subsequent, Sander stated they are going to apply what they discovered in a potential, forward-facing manner.
“We’ll transfer ahead with clinicians and check out it out within the well being system, begin out small and see how effectively it really works,” he advised Fox Information Digital.
“Then, primarily based on the way it performs, we’d think about rolling it out to a broader neighborhood.”
AI screening in a medical setting gained’t occur in a single day — it might take a number of years, Sander stated — however he doesn’t consider it might take so long as producing new cancer drugs.
“If we are able to transfer even a fraction of most cancers care to earlier detection and remedy, it’s going to have an enormous profit — not just for the affected person, but in addition economically, given how costly late-stage most cancers is,” he stated.
“AI-based screening is a chance to change the trajectory of pancreatic most cancers, an aggressive illness that’s notoriously exhausting to diagnose early and deal with promptly when the possibilities for achievement are highest,” Brunak stated, per a press launch printed by Harvard Medical Faculty.
Within the meantime, Sander pressured the significance of understanding household historical past, requesting genetic testing and waiting for early indicators, corresponding to surprising weight reduction or late-onset diabetes.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“Though not as highly effective because the AI methodology, these are nonetheless vital,” he stated.
Sure way of life modifications, corresponding to refraining from smoking, exercising usually and adhering to a nutritious food regimen, may assist scale back threat.
In 2023, about 64,050 individuals within the U.S. will likely be recognized with pancreatic most cancers and about 50,550 will die from the aggressive illness, per the American Most cancers Society. (iStock)
Dr. Castro famous that whereas the research has a number of key strengths, it additionally presents some limitations and considerations, together with the difficult remedy panorama for pancreatic most cancers.
“The complexity of the illness and the necessity for additional developments in remedy choices ought to be acknowledged alongside the potential advantages of early analysis,” he stated.
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
“Additional analysis and exploration of other approaches might assist enhance the effectiveness and generalizability of those fashions, in the end contributing to higher remedy choices and outcomes for sufferers with pancreatic most cancers,” he stated.
The research was funded partially by grants from the Stand As much as Most cancers/Lustgarten Basis, the Novo Nordisk Basis and the Nationwide Institutes of Well being.
Source link
