[ad_1]
Employers are hiring quickly. Dwelling costs are rising nationally after months of decline. Shopper spending climbed greater than anticipated in a latest knowledge launch.
America’s financial system just isn’t experiencing the drastic slowdown that many analysts had anticipated in mild of the Federal Reserve’s 15-month, typically aggressive marketing campaign to hit the brakes on progress and convey speedy inflation below management. And that shocking resilience could possibly be both good or dangerous information.
The financial system’s endurance may imply that the Fed will be capable to wrangle inflation gently, slowing down value will increase with out tipping America into any form of recession. But when corporations can proceed elevating their costs with out shedding prospects amid strong demand, it may hold inflation too scorching — forcing customers to pay extra for motels, meals and youngster care and forcing the Fed to do much more to restrain progress.
Policymakers may have time to determine which state of affairs is extra doubtless, in order that they will keep away from both overreacting and inflicting pointless financial ache or underreacting and permitting speedy inflation to develop into everlasting.
Provided that, buyers have been betting that Fed officers will skip a fee enhance at their assembly on Tuesday and Wednesday earlier than lifting them once more in July, continuing cautiously whereas emphasizing that pausing doesn’t imply quitting — and that they continue to be decided to carry costs below management. However even that expectation is more and more shaky: Markets have spent this week nudging up the likelihood that the Fed would possibly increase charges at this month’s assembly.
Briefly, the blended financial alerts may make Fed coverage discussions fraught within the months forward. Right here’s the place issues stand.
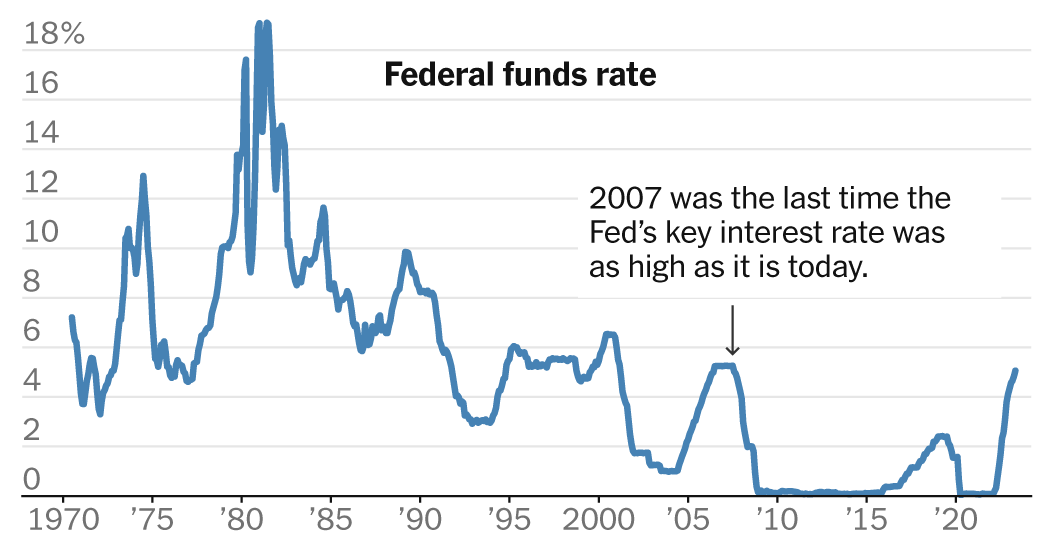
Rates of interest are a lot larger.
Rates of interest are above 5 %, their highest stage since 2007.
After sharply adjusting coverage over the previous 15 months, key officers together with Jerome H. Powell, the Fed chair, and Philip Jefferson, President Biden’s decide to be the subsequent Fed vice chair, have hinted that central bankers could pause to permit themselves time to evaluate how the will increase are affecting the financial system.
However that evaluation stays a fancy one. Even some components of the financial system that usually gradual when the Fed raises charges are demonstrating a shocking potential to face up to in the present day’s rates of interest.
“It’s a really difficult, convoluted image relying on which knowledge factors you’re looking at,” stated Matthew Luzzetti, chief U.S. economist at Deutsche Financial institution, noting that general progress figures like gross domestic product have slowed — however different key numbers are holding up.
Home costs are wiggling.
Larger rates of interest can take months or even years to have their full impact, however they need to theoretically work fairly rapidly to start to decelerate the automobile and housing markets, each of which revolve round huge purchases made with borrowed money.
That story has been difficult this time. Automobile shopping for has slowed because the Fed began elevating charges, however the auto market has been so undersupplied in recent times — thanks largely to pandemic-tied provide chain issues — that the cool-down has been a bumpy one. Housing has additionally perplexed some economists.
The housing market weakened markedly final 12 months as mortgage charges soared. However rates have recently stabilized, and residential costs have ticked again up amid low stock. Home costs don’t depend straight in inflation, however their turnaround is an indication that it’s taking rather a lot to sustainably cool a scorching financial system.
Job alerts are complicated.
Fed officers are additionally waiting for indicators that their fee will increase are trickling by means of the financial system to gradual the job market: Because it prices extra to fund expansions and as shopper demand slows, corporations ought to pull again on hiring. Amid much less competitors for employees, wage progress ought to average and unemployment ought to rise.
Some indicators recommend that the chain response has begun. Preliminary claims for unemployment insurance coverage jumped to the best stage since October 2021 final week, a report on Thursday confirmed. Persons are additionally working fewer hours per week at personal employers, which suggests bosses aren’t making an attempt to eke a lot out of present employees.
However different alerts have been extra halting. Job openings had come down, however edged again up in April. Wages have been climbing less swiftly for lower-income employees, however good points stay abnormally speedy. The jobless fee climbed to three.7 % in Might from 3.4 %, however even that was nonetheless nicely shy of the 4.5 % that Fed officers anticipated it to hit by the tip of 2023 of their newest financial forecasts. Officers will launch contemporary projections subsequent week.
And by some measures, the labor market continues to be chugging. Hiring stays notably sturdy.
“Everybody talks as if the financial system strikes in a single straight line,” stated Nela Richardson, chief economist at ADP. “Genuinely, it’s lumpy.”
Value will increase are cussed.
Nonetheless, inflation itself stands out as the largest wild card that would form the Fed’s plans this month and over this summer season. Officers forecast in March that annual inflation as measured by the Private Consumption Expenditures index would retreat to three.3 % by the tip of the 12 months.
That pullback is progressively occurring. Inflation stood at 4.4 percent as of April, down from 7 % final summer season however nonetheless greater than double the Fed’s 2 % aim.
Officers will obtain a associated and extra up-to-date inflation studying for Might — the Shopper Value Index — on the primary day of their assembly subsequent week.
Economists count on substantial cooling, which may give officers confidence in pausing charges. But when these forecasts are foiled, it may make for an much more heated debate about what comes subsequent.
[ad_2]
Source link