[ad_1]

A brand new analysis research could have discovered a secret to sluggish the method of human ageing and deal with illnesses of inflammatory nature akin to COVID-19, arthritis and coronary heart illnesses.
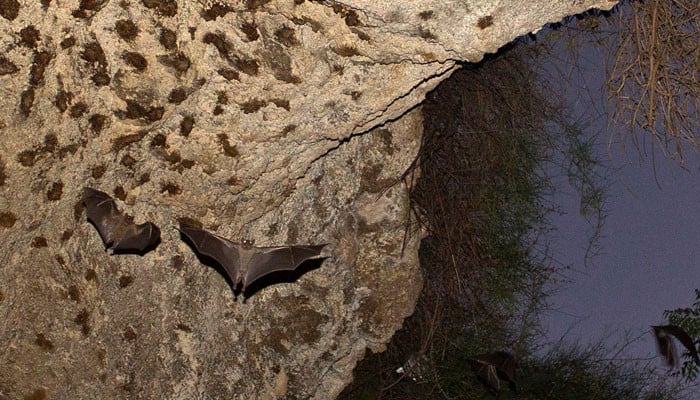
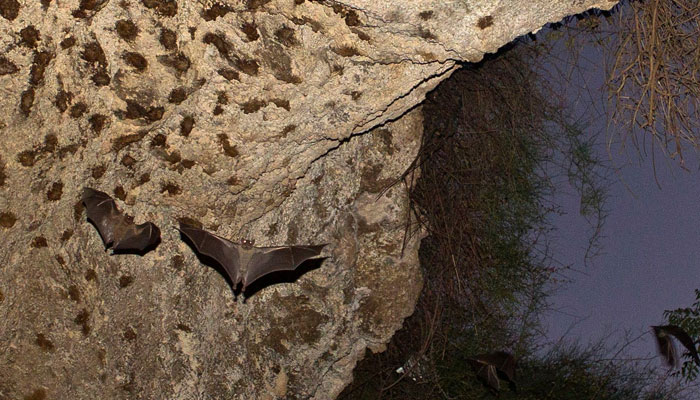
The research revealed that this might occur due to the protein carried by bats.
In accordance with the newest analysis, bats have exceptionally lengthy life spans for small mammals dwelling as much as 40 years. They’ll additionally dwell with deadly viruses together with Sars, Ebola, and Zika with out having any impact on their well being.
Scientists have been capable of decide a contemporary model of a protein known as bat ASC2 which is answerable for suppressing inflammatory responses in bats and will present clarification of their resilience.
In accordance with the research printed within the journal Cell: “When laboratory mice have been genetically modified to hold the protein, the ensuing ‘bat-mouse chimera’ confirmed the identical inflammatory defences as bats.”
In experiments on human cells, the identical consequence was seen.
The staff from Singapore and China wrote within the research: “Our outcomes exhibit an essential mechanism by which bats restrict extreme virus-induced and stress-related irritation with implications for his or her lengthy lifespan.”
The staff additionally stated: “When the bat ASC2 — solely barely totally different from our personal — was examined on human cells they too turned extra resilient, demonstrating its therapeutic potential.”
“The findings present new insights and techniques to fight ageing and inflammatory illnesses in people,” they added.
The analysis chief Dr Linfa Wang, a professor of rising infectious illnesses at Duke-NUS Medical College, instructed Telegraph upon being requested whether or not bat ASC2 might maintain the reply to longevity and decreased mortality from viruses in people: “Sure. It will not be the one issue, as biology isn’t so simple as one molecule or one pathway. However the total dampening of irritation probably performs a task in well being ageing in bats.”
Dr Wang, who, in 2005, helped to determine that bats have been the pure reservoir of Sars viruses, additionally famous: “The brand new analysis might ultimately result in human medicines that ‘mimic ASC2’, and could possibly be used to deal with a variety of viruses that set off an inflammatory response.”
“We’ve filed patents primarily based on this work and are exploring business partnerships for drug discovery. We hope to develop a brand new class of anti-inflammatory medicine for inflammasome-driven human illnesses,” stated Dr Wang.
As per the findings, the mortality charge from a deadly influenza virus dropped from 100 to 50% amongst these with the ASC2 adaptation. The protein additionally “considerably inhibited” the Zika virus within the bat mice.
“[It’s] very thrilling to see ASC2 within the long-lived mole-rat as nicely, however what’s the key stress in mole-rat that triggered the ‘convergence’ evolution as we see in bats stays to be elucidated,” stated Dr Wang.
Prof Stuart Neil, a professor of virology at King’s Faculty London who was not concerned within the research, stated you will need to assist clarify “whether or not there are particular options of the bat immune system that enable them to tolerate an infection with so many seemingly nasty viruses.”
However he added that extra analysis is required to substantiate whether or not ASC2 is answerable for lengthy lifespans in bats — one thing that shall be tough to find out.
“Nevertheless, understanding how bat ASC2 shuts down [the] irritation could definitely enable the rational design of extra targeted therapeutics for continual inflammatory illness. Whether or not such understanding may have a common preservative impact on lifespan is anybody’s guess,” he stated.
Professor Gilda Tachedjian, head of Life Sciences on the Burnet Institute in Australia, added: “They present proof of idea that bat ASC2 protein can goal the inflammasome thereby dampening markers of irritation in vitro [cell culture] and in a transgenic mouse mannequin.”
“Whereas the findings of this research are intriguing, extra work is required to translate these findings into new therapies that can be utilized in folks to scale back mortality from viruses or enhance longevity.”
[ad_2]
Source link



